Introduction to databases
Concepts
flat-file database
Databases that can only contain one table
Multi-valued
http://www.attcanada.net/~kallal.msn/Articles/fog0000000006.html
ISAM
Indexed Sequential Access Method
key/value ("hashing")
""relational" is the key feature of relational databases: they are interesting not because of a given element (i.e. row in a table) on its own but because of the relations between rows and tables. If you don't need relations, then there's no reason to use a relational DB. The whole point is to use multiple tables ;) Otherwise you just have a flat file."
... or has engines like SleepyCat :-)
relational
object-oriented
XML
Keys
Primary, foreign, referential integrity
Indexes
Views
Normalization
First, second, third normal forms
Transactions
Ie. bunch of SQL instructions that sit between a BEGIN and COMMIT statements
Tuning
SQL
Commands
Triggers
Stored procedures
Atomic transactions, commit/rollback
Pessimistic/optimistic locking
Cursor
Joins
Inner (symetric, ie. returns all the rows common to the tables used; inner join, cross join, equijoin), outer join (asymetric, ie. only some of the rows are returned; outer join, left join, right join), self join (using only one table, and creating temporary aliases)
APIs
MDAC
(From MS) The Microsoft Data Access Components are the key technologies that enable Universal Data Access. They include ActiveX Data Objects (ADO), Remote Data Service (RDS, formerly known as Advanced Data Connector or ADC), OLE DB, and Open Database Connectivity (ODBC).
UDA
Universal Data Access. Here's the UDA architecture as seen on MS site:
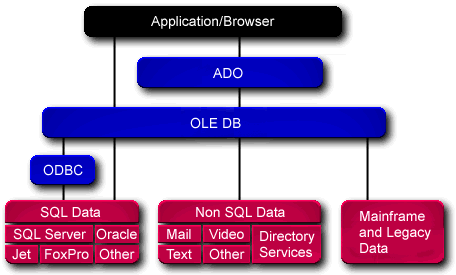
OLE DB + ADO
OLE DB is a set of COM interfaces specific to access data sources; OLE DB providers are usually accessed through ADO, which encapsulates OLE DB to expose a simple interface through methods, properties and events.
RDS
(MS) Remote Data Service (RDS) is a feature of ADO. RDS delivers a new Web data access technology that allows developers to create data-centric applications within ActiveX®-enabled browsers such as Microsoft® Internet Explorer.
DAO/RDO
Here's a comparison of OLEDB-ADO and DAO-RDO as seen on MS site:
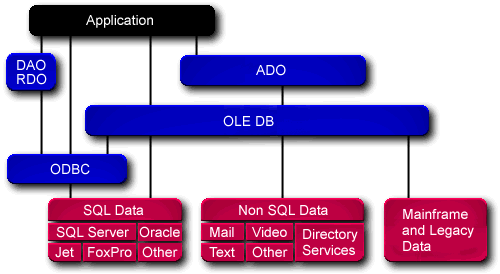
?????
ODBC
(MS) Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a widely accepted application programming interface (API) for database access. It is based on the Call-Level Interface (CLI) specifications from X/Open and ISO/IEC for database APIs and uses Structured Query Language (SQL) as its database access language.
DSN = Data Source Name, ie. name given in ODBC to a connection profile. User DSN = user-specific connections; System DSN = system-wide connections, ie. any user who logs on to this computer can use those DSN's; File DSN = access to DSN definition files (*.DSN)?; ODBC Drivers = list of drivers installed
ODBC configuration done through Control Panel.
JDBC
Implementing concurrency
If your database doesn't handle concurrent accesses, you'll have to implement this in your application. Three possibilities are available:
- pessimist locking: A lock is created before any change is made, keeping other hosts or processes from making any change
- optimist locking: use a variable to check whether data were changed between the time you read data, and when you're about to record your changes. If someone else made changes in the meantime, either discard your changes, or let the user decide
- last in wins: You don't care if another host or process made changes between the time you read data, and when you made your changes
From optimistic locking:
- Anyway... back to the specific question... the way I've done it in the
past is to store the timestamp in the Value and View objects (you can store
the timestamp in a hidden field on the jsp). Then when you save the object
you do:
- update table foo set x=? where id=? and timestamp=?
- Check the return to see how many rows where affected. If non were affected then you basically have a stale update (either the timestamp was changed in the interim or someone deleted the row out from under you). I've used triggers or explicit setting of the timestamp in the past. Note that it does not even need to be a real timestamp... it could be a verion number too. In one application we were keeping audit trails for all changes and we decided to use a sequence instead of a timestamp.
From VFP 8.0 and Sql Server: implementing pessimistic locking:
- Because we're still not sure of how to best implement sql server locking with a VFP front end, my boss has suggested a customzied locking design. His idea is that VFP would write to a central "lock" table when a user decides to modify a record. Then if another user comes in and tries to modify the same record, his session would check the contents of the central "lock" table to see if the first user is already modifying the same record.
From Code Charge:
- The first method you describe the most common way on implementing concurrency.
Grab the last update datetime when it come to perform the update check this
field and action the update if the datetime has not changed.
An alternative to actually doing the check before the update statement(that's one extra round trip remember), is to use the Username and Datetime as part of the where clause, then to check the number of records modifed by the update statement. SQL server for example provides @@ROWCOUNT to give the number of rows affected by the last statement.
An alternative method that we are using to write custom update that only updates the ACTUAL changes the user has made. So if User A changes The phone number, and user B changes city only one field is updated per user, the script that CCS generates out of the box doesn't handle this and you will need to write code to implement. This method still has shortcomming but it's an alternative. - To provide for the memo-type (textarea) problem, one could actually show a message to the user "memo being edited by user: XYZ" thereby triggering the users to contact each other (in a closed group) and agree on a change policy.
- In our support system we use somewhat of an emulated pessimistic locking. We use "date_locked" and "locked_by" fields to track who locked each record and when. The records aren't locked automatically but the user can view a record and then click the "Lock" button to indicate that he/she is making concious decision to lock and edit the record. The record stays locked for X amount of time or until the record is updated. However, other users can press the "Unlock" button and start making their own changes, which in our situation isn't very dangerous because the main record isn't actually edited, just new support responses are added.
From Handling Concurrency Issues in .NET by By Wayne Plourde
- The only way to prevent concurrency errors is to lock the records that
are being edited. There are two basic approaches towards locking - optimistic
and pessimistic. One would consider an optimistic locking scenario when
the likelihood of a concurrency condition is low. This is usually the case
in systems where the activity is primarily additive, like an order entry
system. On the other hand, one would consider pessimistic locking when the
likelihood of a concurrency condition is high. This is usually true of management
or workflow-oriented systems. [...]
- One of the drawbacks of using pessimistic locks is that locks can be set then forgotten. Therefore, you may need to provide some way for the application to recover so that the entity in question can be accessed again. One approach is to allow locks to timeout. In this case, you would need to provide a DateTime data field to track when the lock was set. Then if the lock is older then some predetermined amount of time, you would ignore it, allowing users to access the record for updates.
- Another approach is providing the ability to define permissions to allow an administrator to override or clear previously set locks. This may be especially important if you are not providing timeouts.
To read:
Embedded databases
Embedded means that the database component should ideally live in a single DLL containing both the client and server parts and save its data in the filesystem. Obviously, this means that the database server offers no data protection from external access, either locally or through the network. In other words, those lightweight solutions that offer no server process are meant for single-user usage since the only protection comes from the OS.
SQL
Ocelot
MySQL
- Embedded MySQL Server in PowerBasic
- As of June 2003, not usable directly from VB due to its lack of static linking to DLLs (ie. at compile-time). Could shell to a PowerBasic EXE to make the actual calls
- The DLL is located in C:\mysql\Embedded\DLL\release\libmysqld.dll
FireBird
- An embedded version is now available in release 1.5. The API is supposed to be the same as the c/s version
- http://firebird.sourceforge.net
- Javier Soques wrote a C++ wrapper to let VB developers use the embedded version of FireBird : http://fbdll4vb.sourceforge.net
Speedy
- http://www.geocities.com/wabhar/
- No DLL provided, must compile C source code
- speedy1 is the embedded version; speedy is the TCP-based client-server version
- speedydb is the SQL engine
- speedysh is the command-line client
- speedyst is used to manually stop speedydb
- Use speedysp to automatically stop speedydb when Windows shuts down
- DB-Viewer is a GUI application to view/change Speedy-database contents, DB-Designer is a GUI application to design Speedy-databases
- DB-Preparator generates database access functions, and DB-Generator transforms database description formats
- To check out performance: launch the server by opening a DOS box and running speedydb, create a database with "speedysh CREATE dirdb", and run the test application with "dbdir", whi inserts 30000 rows (each a pair of integers) and then accesses the rows in various ways
- The Speedy.dat-directory contains all information about the database
- No network support?
hSQLDB
- Built in Java, 160K, requires JVM
- Comes in embedded and server versions
- http://hsqldb.sourceforge.net
SQLite
A free C library that implements a DBMS. Comes with a standalone command-line access program that can be used to administer the database. Available here. Doesn't provide a server process to allow safe simultaneous write access, but relies on the file system locking mechanisme instead. Very fast when used with transactions, on par with MySQL when used in asynchronous mode, much slower than MySQL and PostgreSQL when used in synchronous mode. A mailing list is available at Yahoo : http://groups.yahoo.com/group/sqlite/
To import tab-delimited records (ie. CSV):
- sqlite.exe mydb
- create table test (i integer primary key, name);
- copy test from 'import.txt';
If the CVS data don't have a primary key, here's a trick to import those into SQLite:
- sqlite.exe mydb
- create temporary table table1 (...);
- copy table1 from 'import.txt';
- create table table2 (keyfield INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, ...);
- begin;
- insert into table2 select null, * from table1;
- commit;
In case you need reports, ie. long lock on a DB, you could create a temporary table, and read from this database instead (http://groups.yahoo.com/group/sqlite/message/3565).
- A VB6-compatible DLL
- VB5-compatible wrapper (from Steve O'Hara at Pivotal Solutions)
- SQLite Assistant and SQLite Explorer
- ViewStruct
- EasySQLite
- Discussion on VDLite
- PowerBasic wrapper (part of Visual Designer)
- SQLite Framework
- The start of a PowerBASIC SQLite framework
- The C language interface to the SQLite library
- Some SQL links
CQL++
- Comes in two versions : single-user, and c/s
- http://www.cql.com/
TurboPower FlashFiler
- Also available in server mode. Delphi & C++
- http://sourceforge.net/projects/tpflashfiler/
Maverick
- Technically, not SQL but rather an open-source clone of the MultiValue Database (MVDB or MVDBMS, originally known as the Pick Operating System), more flexible than RDMBS'
- Written in Java, so requires JVM
- http://www.maverick-dbms.org/
Hashing, non-SQL
db.*
- ITTIA
- ITTIA launches db.* embedded database By Linda Cole
ZODB
- Core of Zope
- http://www.zope.org/Wikis/ZODB/
My little base
http://www.mylittlebase.org : Delphi or C++
EZTree
It is up to you the programmer, to make sure that you always pass your record data with the same length for each record and the same length for the Index Key.
Cheetah
Light, closed-source DBMS from Planet Squires.
XDB
http://linux.techass.com/projects/xdb/ : C++
BerkeleyDB
Open-source. Generates hashed files, hence poor man's storage system. Available here.
Tsunami
Light (one DLL), closed-source solution available here.
DvBTree
Available here.
CDB
- From Dan Berstein
- http://cr.yp.to/cdb.html
MetaKit
http://www.equi4.com/metakit/ : C++, Python, Tcl
DynDB
http://www.ohse.de/uwe/dyndb.html
Goods
- Generic Object Oriented Database System
- http://www.ispras.ru/~knizhnik/goods.html
PureDB
http://www.pureftpd.org/puredb/
Free Database Engines
TurboPower FlashFiler
- FlashFiler is a client-server database for Borland Delphi & C++Builder. It features a component-based architecture & the server engine can be embedded in your applications. FlashFiler is easy to configure, performs well, & includes SQL support
- http://sourceforge.net/projects/tpflashfiler/
Speedy
GNU SQL server
- http://www.ispras.ru/~gsql/
- Latest release : 28 Sept 98...
Adabase PE
- Personal Edition : Adabas D (limited to 3 users, 1 CPU, 100 MB data space) +/- 75 294 169 B
- http://www.softwareag.com/adabasd/AdabasD/AdabasD12.htm
PostGreSQL
Open-source solution available here.
SAP DB
Borland Interbase
An open-source version is available here, here and here.
FireBird Interbase
Enhanced version of Interbase. Available here. Because Borland's open source efforts regarding InterBase never really took off beyond prime release of the source code and the company returned its focus to closed commercial development, Firebird became THE Open Source version of InterBase. Yet more information here.
Jet
A complete ISAM relational database engine that is 9/10ths of Microsoft Access, for free. it's preinstalled on Windows 2000. Does not scale. General-purpose interface.
MSDE
Scaled down version of the SQL 7.0 engine, royalty free, and optimized for up to 5 concurrent users
MySQL
Open-source solution available here
MDBMS
- http://www.hinttech.com/
- For Unix
OpenIsis
Commercial Database Engines
Besides the usual suspects (Oracle, DB2, Sybase SQL Server, MS SQL Server, etc.)...
Advantage
- "Advantage Local Server" is free, and the server-based version is commercial
- http://www.advantagedatabase.com
mSQL
- Mini SQL 3.x - Single License USD $250
- http://www.hughes.com.au
CodeBase
Available here.
Informix SE
http://www-3.ibm.com/software/data/informix/se/
APIs
DAO
Designed to access the Jet database. Can't retrieve non-relational data. Being superseded by ADO, and ADO.Net.
RDO
ADO
Enhancement to DAO. Requires ADO drivers. Used to access SQL DBMS's. Unlike ODBC, can access both relational and non-relational data.
OLEDB
Used by ADO to access actual data.
ODBC
Limited to relational data.
Q&A
What is MDAC used for?
Basic database-related stuff that you need to install in Windows before installing such and such database-specific ODBC driver?
Temp stuff
- From: Jon Rista (jrista@hotmail.com)
- Subject: Re: Should ODBC be used ?
- ADO is faster if you use it properly. There are lots of little "things" to be aware of when using ADO, such as lock type, cursor location and type, etc. Proper combinations of different ADO settings can result in very good performance.
- The best results for SQL Server come when you use the native OLEDB provider for it. When you use the OLEDB provider for ODBC, you add at least one extra layer of abstraction between your presentation tier and the data itself. This decreases performance. Whenever possible, you want to use the native OLEDB provider for SQL Server, as it provides direct access to the database, no intermediate layers (other than ADO) are required. If you use a properly configured connection with a database with proper indexes and constraints, SQL Server 2000 can be faster than Oracle, and significantly faster than IBM DB2.
- Subject: Re: Should ODBC be used ?
Resources
- SQL for Web Nerds by Philip Greenspun
- A gentle introduction to SQL
- Database Essentials
- Comparing Databases
- Good tutorials on databases
- (French) Quand faut-il investir sur le client/serveur ?
- (French) Introduction aux bases de données
- (French) Le langage SQL
- (French) Le langage SQL
- (French) SQLPro - Developpez.com (forum Langage SQL)
- Understanding SQL Joins
- An Introduction to Database Normalization
- A practical approach to database theory
- DeZign for databases
- Database Debunking - Dispelling persistent prevalent database management fallacies
- Introduction to Structured Query Language
- Evolutionary Database Design